| Guideline: Business Plan |
 |
|
| Related Elements |
|---|
What and Why: Business Plan is predominantly a decision making tool. It is a comprehensive and holistic way to plan an overall product or IP Solution business. It is a formal statement of all the key elements of the envisaged business. It describes the background of the business around product/ IP solution, business goals set for the product / IP solution, plan for achieving the set goals and reasons for believing that set goals can be achieved. It contains all the key information that the Management requires to take a Go/No Go decision. Business plan typically contains what the IP solution, and what market opportunity it addresses with providing an overview of the market environment (targeted customers, competition, and ecosystem). It defines the intended value proposition and market positioning for the IP solution. The IP solution business objectives (like market share or number of deals signed, geographic footprint extension, 3 and 5 year expected revenues & margin etc) are set in the document. It also presents how it will successfully be achieved (planning, go-to-market description, risk analysis…) and also identifies the key resources required. Hence it is critical to ensure that all the aspects of the IP solution business are thought through. It also serves as a baseline to measure all future results. Who, How and Best Practices: The process of business plan for IP solutions in Capgemini has two stages:
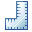
In stage-1, Product management Strategist or Head shall be responsible for preparation of business plan as a document with support from other members of the IP team. This process shall be initiated after having concrete IP solution idea and completed with initial market opportunity analysis. Product strategist shall use the business plan template provided. Refer to the Business Plan e-learning module at Capgemini University for detailed understanding of the Business plan preparation. Stage-2 is the process of submission of business plan and its approval by the management. It has three levels, one at Business unit level, two at Strategic business unit level and three at Group level. IP solution Product head/strategist must seek approval of business plan for investments into any IP solution. It is a mandatory step. BU leader decides to seek approval or inform SBU leader based on the type, investment and implications of the IP solution. At group level the review and approval process is performed by IP Board. Seeking approval from IP Board is mandatory for investments in excess of 300KEuro or efforts of 500 person-days, else for investments less than the above threshold it is necessary to inform such investment decisions to the IP Board.
At Business Unit level Product head/strategist (IP solution owner) shall contact their local BU IP Champions to check if a formal approval process exists or not within their Business Unit (refer to list of IP Champions is available in the Who’s Who of the Talent IP Hub). IP Champion facilitates the review process. During this review, BU approval team reviews the business plan and advises on next steps. The recommended members of BU review team include BU Leader, IP Solution owner/head/strategist, IP Solution project Leader’s direct manager, BU IP Champion, CSO and any Sector Leader impacted by the IP Solution, IP Specialist of the BU Legal Team (each BU has an IP Specialist in their Legal Team) and SBU representative. At Strategic Business Unit (SBU) level, there are 3 possibilities which can arise after discussion with the BU Leader.
At Group level, any IP Solution project involving an investment in excess of Euros 300 thousand or 500 person-days must be submitted for IP Board approval. IP Board must be informed of IP Solution Projects launched with a lesser investment. Product head/strategist shall contact the IP Central Team through BU IP Champion. IP Central Team shall help to organize a presentation for the IP Board. In this process IP Central team helps in Planning, Guidance and pre-IP Board reviews. The IP Board presentation template shall be used for the presentation. The IP Board presentation should be crisp & straight to the point, focusing on key elements. It should have a maximum 7 to 10 slides, describing the Context (summary of market opportunity, Capgemini legitimacy, background of the IP solution – is it derived from a client project, worked with partner etc.), IP Solution description & value Proposition, Go-to-market, Financials (revenues, cost & profitability) along with investments and pre-requisites. IP Board review can happen through a plenary session on quarterly basis or through an adhoc restricted session with a limited number of IP Board members if there is urgency, or if the project is very specific to only one or two BUs Notes:
References:
|